In the construction industry, thermal insulation materials are construction materials used to reduce heat transfer between materials or structures of varying temperatures.
Heat reduction is the primary reason why thermal insulation materials are being used in houses and buildings whether for commercial or industrial purposes. The use of thermal insulation materials greatly affects the following:
- Air cooling or air conditioning inside the building or houses (HVAC design)
- The performance of particular construction material or structure that requires thermal insulation such as roofs, damp-proof courses, waterproof membranes, related joints or sealants, and others.

Thermal Insulation Materials for Buildings – General Requirements
The general requirements for thermal insulation materials commonly being looked for are the following:
- Testing for the quality.
- The compliance with the fire requirements.
An additional requirement may be added depending upon the type or condition of the project.
On the other hand, all the reference that has to be used must be in accordance with the recognized standard either British standard or American standard.
Submittals – Thermal Insulation Materials
Below are the submittals along with all relevant attachment which needs to be provided by the supplier or contractor to the client or client representative.
- The submittals must conform to the general requirements.
- The submittals which have to be submitted by the contractor shall include the manufacturer’s literature and technical data for each type of thermal insulation materials, corresponding adhesives, and tapes.
- The contractor shall submit to the Engineer (or client’s representative) the details of all thermal insulation materials to be installed. The information shall include (a) type of insulation, (b) dimensions of insulating materials, and (c) thermal insulating properties. All corresponding standard references shall be included along with the submittals.
Common Types of Thermal Insulation Materials for Building
Depending on what type of structure or conditions, different types of insulation may be specified. One type of insulation shall be used in a particular area if possible.
Below are the insulation material types and its corresponding materials commonly used.
1. Cavity Wall Insulation.
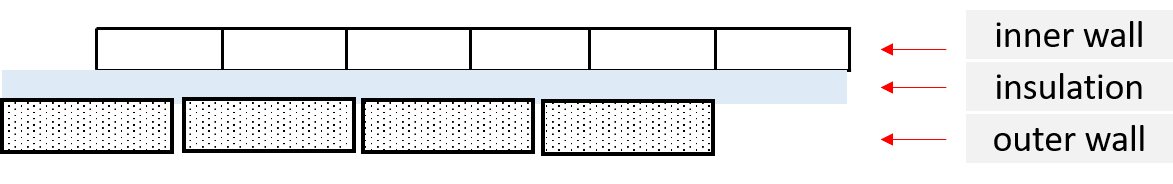
- Polystyrene board. Relevant provisions of BS 3837 has to comply.
- Polyurethane board or polyisocyanurate. It must be in line with the provisions of BS 4841 and must be faced with a vapor barrier.
- Mineral fiber board. It shall comply with BS 1142 and must be used with a vapor barrier.
- Foam system insulation. If it is to be used in the cavity wall, it must be in accordance with BS 5617 and BS 5618.
The cavity wall is composed of an inner wall and outer wall with a gap between them usually filled with insulation or protection materials.
Perm rating is the measure of water vapor permeability of a material. It must not be greater than 0.5. A water vapor barrier is also called water vapor retarder.
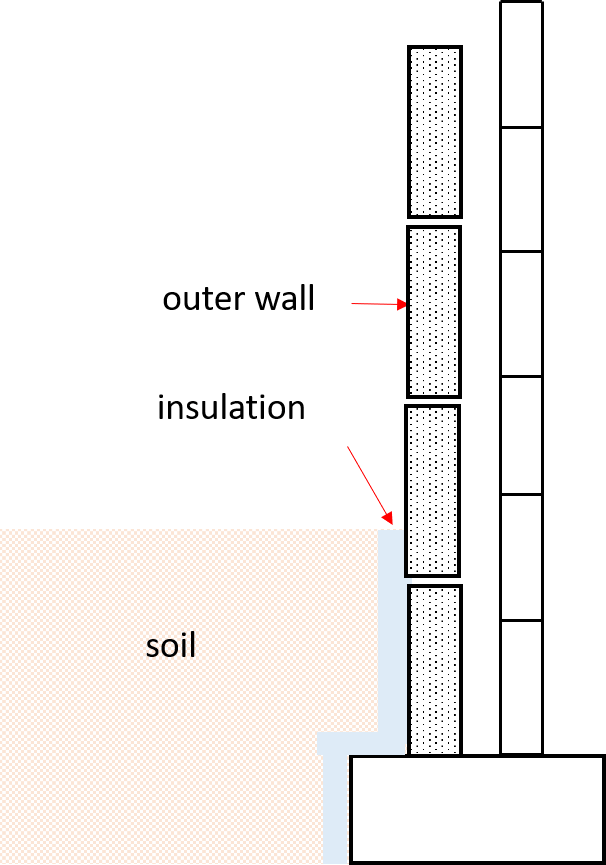
2. Perimeter Insulation
- Polystyrene board. Insulation on the surface of the structure in contact with soil shall comply BS 3837 and BS 8216.
- Sprayed lightweight mineral coating. If it is to be used, they shall be in accordance with BS 8216.
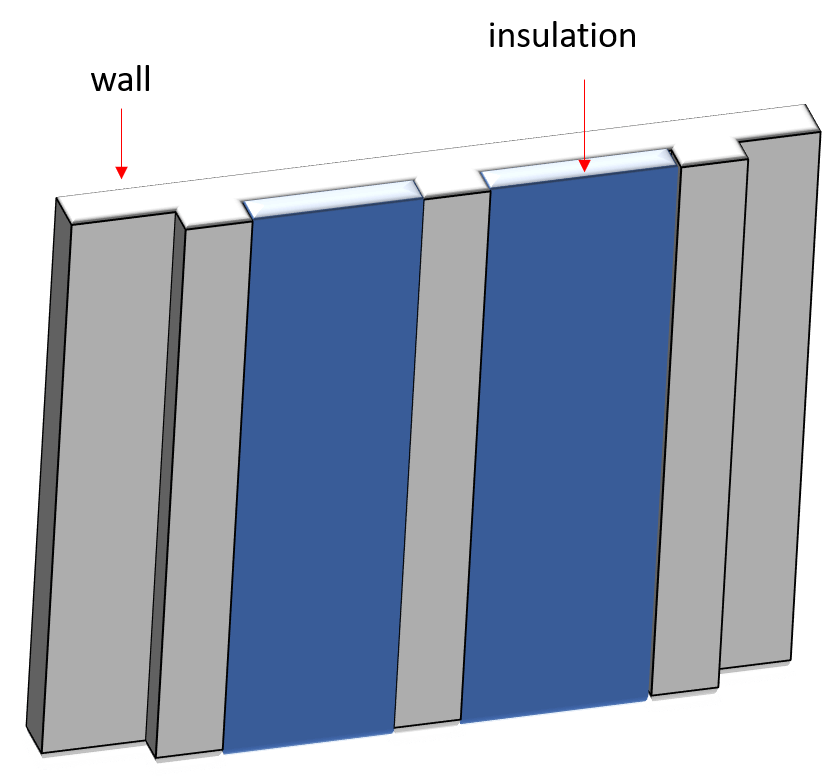
3. Furring Insulation or External Framing Insulation
- Batt or Blanket type insulation (typically made of fiberglass). For exterior wall insulation, it must be provided with protection and subject to the approval of the client or client’s representative.
- Mineral fiber board. It shall comply with the provision of BS 6676 Part 1 and Part 2.
4. Masonry Fill Insulation
- Vermiculite insulation. Relevant provisions of BS 8208 has to comply.
Accessories or fastener for masonry fill insulation such as staples or nails, screws, and steel impaling pins shall comply with relevant British standard provisions.
5. Rigid Insulation
- Mineral fiber board. The relevant provisions of BS 6676 Part 1 and Part 2 has to be checked.
6. Roof Insulation
- Lightweight concrete screed. A foamed concrete type that acts as an insulating layer. The density, thermal conductivity, and all other details must be in accordance with the technical specification of the project.
- Polystyrene Foam or Board. Thickness, thermal conductivity, types, and other details shall be in line with project specification.
There are other types of insulation materials which are not mentioned above.
For now, let’s take a look at the sample specs of roof insulation material obtained from one of the projects in the Middle East.
(a) Lightweight concrete screed or approved type of foamed concrete.
- The density of lightweight concrete must be between 1040 kg/cubic meter to 1120 kg.cubic meter.
- Thermal conductivity K value must 0.302 W/m degree Celsius.
- Chemically inert, stable, impermeable, and organic.
- 28 days compressive strength shall not be below 2.0N/sq.m.
- A layer of cement and sand shall be 1:3 mix topped 10mm above the screed
(b) Extruded polystyrene rigid foam or equivalent.
- Thickness shall not be less than 40 mm and specified thermal conductivity shall be achieved.
- Resistance to rotting
- high resistance to thermal cycling
- good dimensional stability
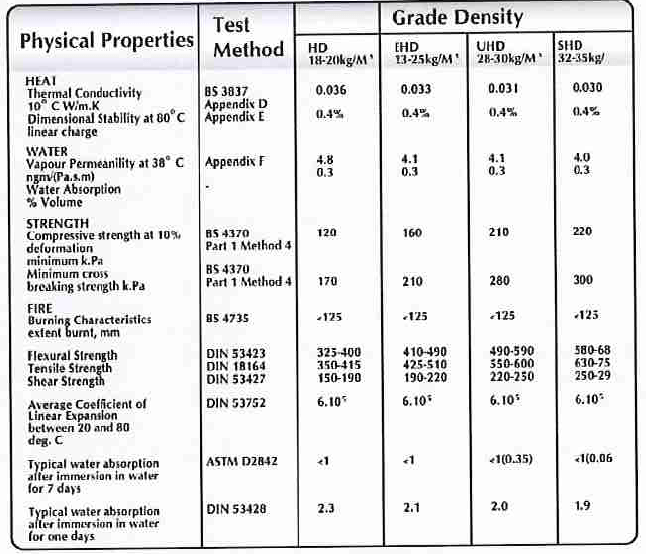
Meanwhile, below is sample thermal insulation product data sheet.
Checking the Standard Reference
The standard reference for the thermal insulation materials which was considered in this post is all British standard.
Take note that below are some references only of thermal insulation materials for buildings. All relevant codes must be can be found usually in the project’s technical specification.
- BS 874 (Methods for Determining Thermal Insulating Properties)
- BS 3837 – To determine the thermal conductivity, dimensional stability, vapor permeability.
- BS 4370 – To determine the compressive strength and minimum cross breaking strength.
- BS 4735 – To test the burning characteristic of cellular plastics and rubber materials.
- BS 6203 – For fire characteristic and performance of expanded polystyrene materials used in building application
- BS 4841 – For rigid polyurethane or polyisocyanurate foam for building applications
- BS 5250 and BS 5803 – For condensation control requirement where insulation is used at roof surfaces, exterior wall, or underground.
Depending on what kind of materials or structures, all the references must be specified in the scope of work.
If you have some question, clarification, additional information, or any helpful insights related to the above topic, please free to drop it in the comment section below.
Thank you for visiting our page.
Do you want to learn more about how to check other materials? Please try to check other topics below:
1. How to check ready-mix concrete pouring?
2. How to check backfilling materials?
